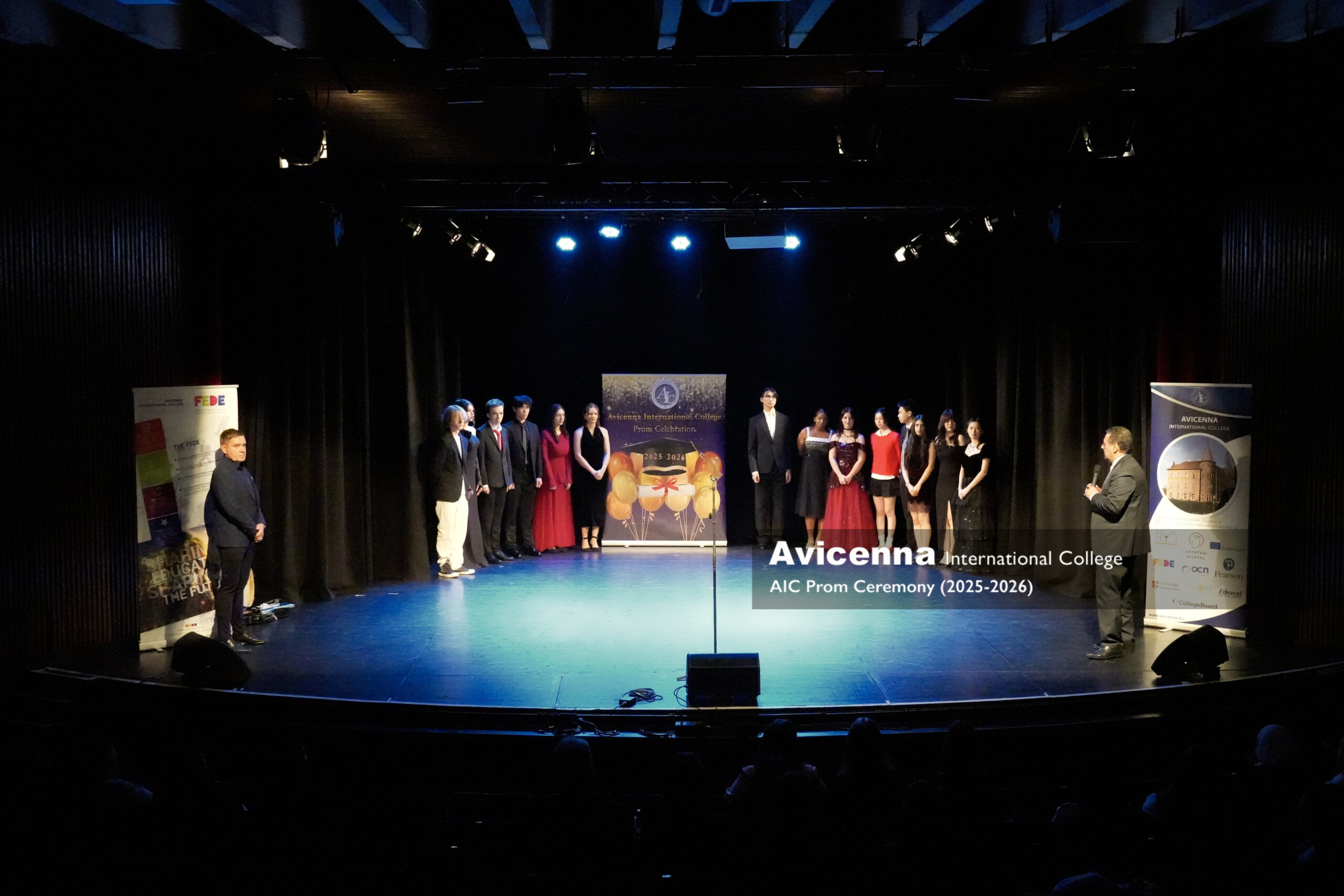
AI and the 6Cs for Future-Ready Teaching,
26-31 May 2025
Written by: Steve Szabó
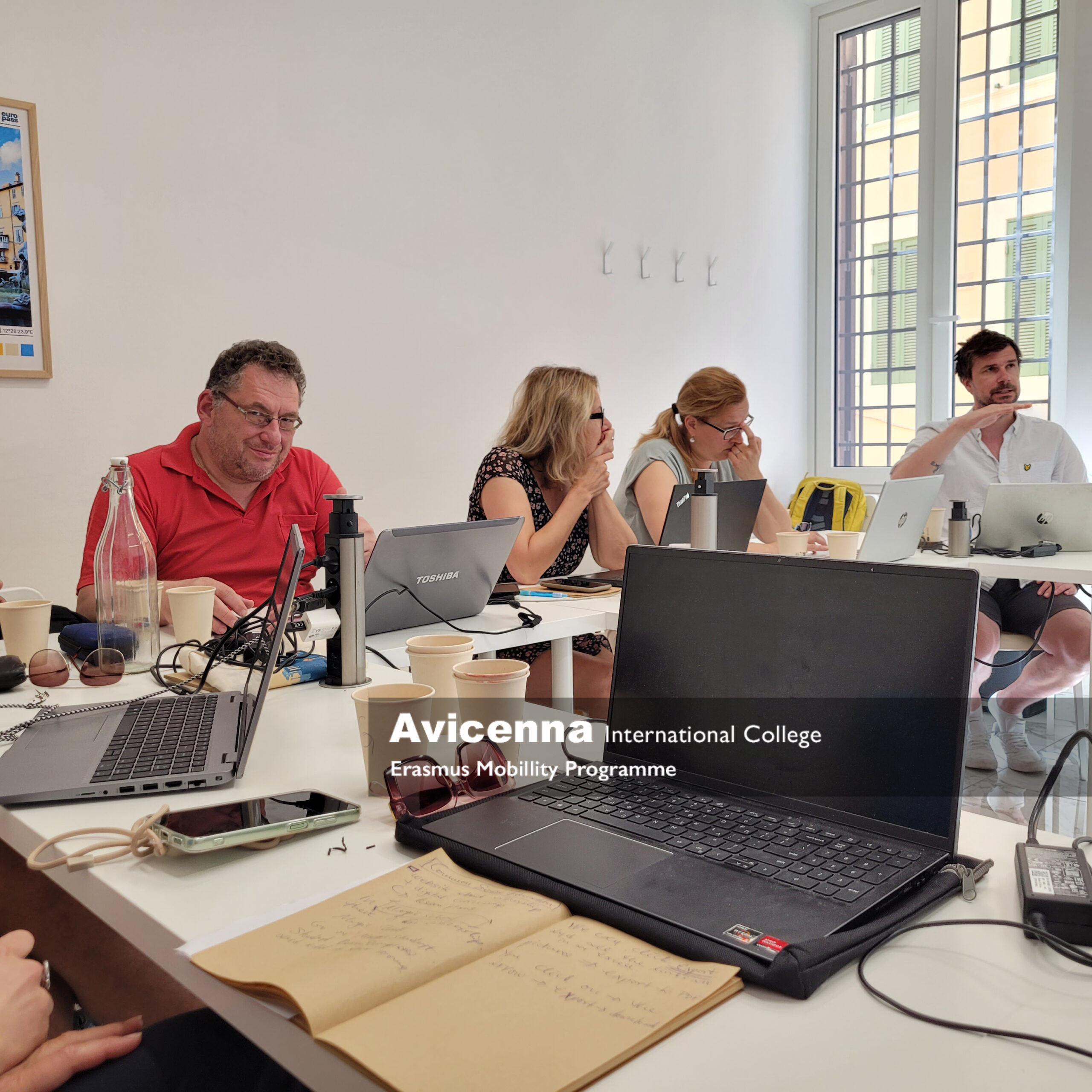
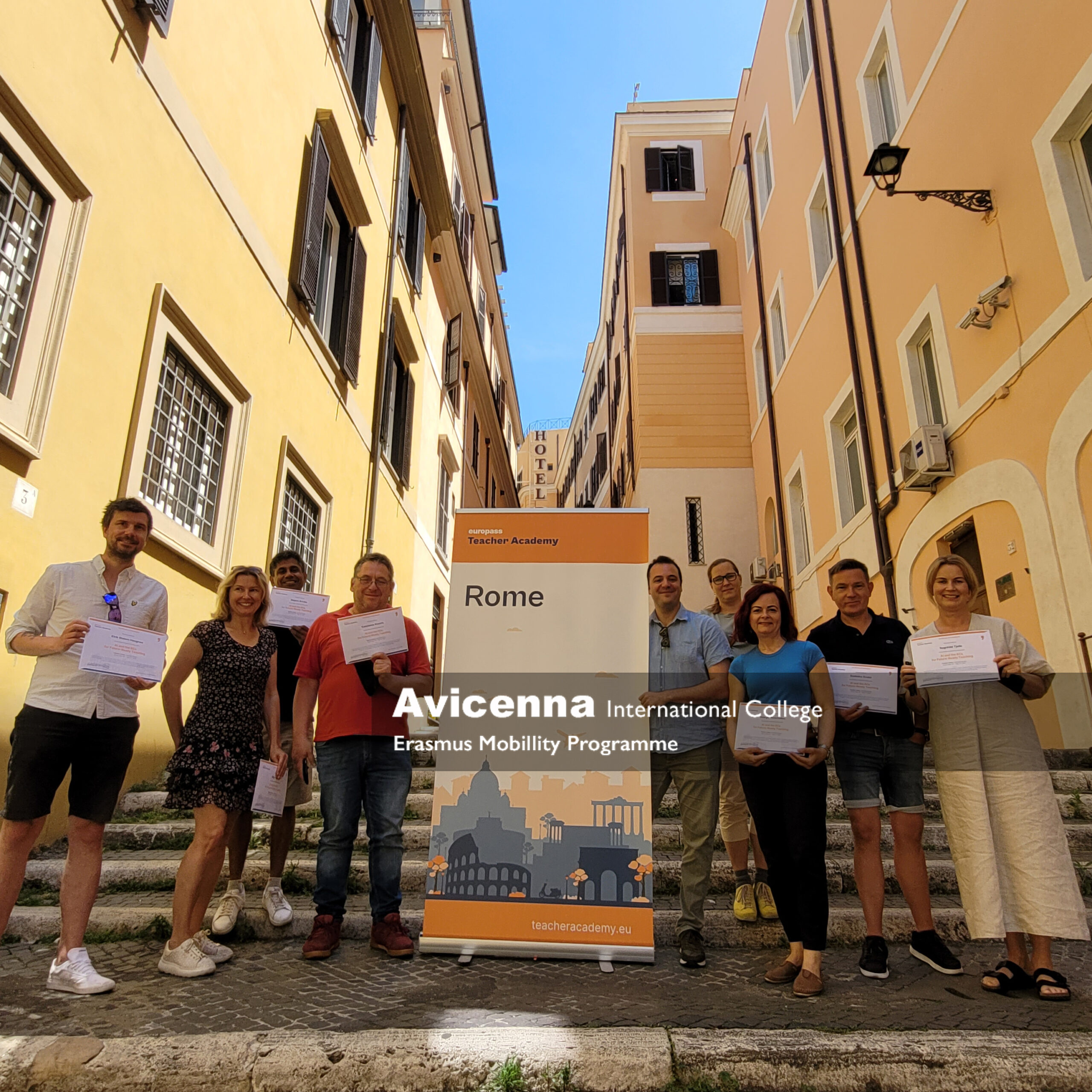
In the heart of Rome, where ancient and medieval history blends seamlessly with modern life, eight enthusiastic educators from across Europe gathered for a transformative five-day Erasmus+ teacher training course on the integration of Artificial Intelligence in high school education. The course, hosted in a new and modern learning centre of Europass Teachers Academy not far from the Colosseum in Quirinale, was led by Leonardo, a Roman linguist and digital learning expert with a deep passion for educational innovation. Participants hailed from Cyprus, Greece, Germany, Czechia, Norway, and Hungary, each bringing their own perspectives, school contexts, pedagogical challenges and laptops for this AI training.
Learning Together in the Eternal City
The course focused on equipping teachers with practical, ethical, and creative strategies for integrating AI tools into their classrooms. From day one, the atmosphere was collaborative, warm, and intellectually stimulating. Leonardo opened the sessions with a bold statement: “AI is not the future- it is the present. Our students are already living in it.”
Throughout the week, we engaged in hands-on activities and case studies that explored how AI tools/bots like ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, Copilot, Claude as adaptive learning platforms, and image recognition software can support teaching and learning. While some of us had previously dabbled in AI, others were newcomers, approaching the topic with curiosity and a touch of scepticism.
Leonardo’s interactive teaching style encouraged peer discussion and experimentation. We explored the capabilities of generative AI to support lesson planning, differentiate instruction, and boost engagement, particularly in multilingual or mixed-ability classrooms. For example, one participant from Germany demonstrated how students used AI to simulate interviews with historical figures, enhancing both language skills and historical empathy.

The Pros and Cons: A Balanced View
As we delved deeper into the potential of AI, the group openly discussed the double-edged nature of these technologies. On the positive side, we saw how AI tools can personalize learning, assist neurodivergent students, and automate repetitive tasks, giving teachers more time for meaningful interaction. Participants shared how their students used AI for formative feedback on essays, developing their writing skills in a more autonomous way.
However, we also explored the limitations and challenges. A key concern was over-reliance. Some students use AI to generate assignments without understanding the content. This creates a false sense of mastery and can hinder genuine learning. Moreover, the question of data privacy loomed large- many AI tools collect user data without clear consent.
Several participants shared stories of colleagues resistant to AI- not from lack of understanding, but from a deep concern for student development and academic integrity. This scepticism is not without merit. As one Norwegian participant put it: “When students copy-paste AI-generated work, we are not assessing their thinking, only their ability to prompt a machine.”
To address this, we discussed AI-resistant assessment strategies, such as oral exams, portfolio work, real-world projects, and metacognitive reflections. These methods ensure students are evaluated on their own understanding, creativity, and effort. As Leonardo pointed out, “The more authentic the task, the harder it is to fake.”

Ethics, Equity, and the Human Element
The course also highlighted the ethical dimensions of AI use in education. We questioned the equity of access: while some students use advanced tools at home, others may lack internet access or digital literacy. There was also discussion about algorithmic bias and the importance of teaching students to think critically about the tools they use.
One of the most profound takeaways from the course was the reminder that AI should not replace the teacher, but rather empower them. The emotional intelligence, mentorship, and moral guidance that educators provide cannot be replicated by algorithms.
Leonardo guided us in aligning AI integration with the 6C skills– the core competencies students need for success in the 21st century:
- Collaboration – AI can foster teamwork through shared digital workspaces and collaborative problem-solving tasks.
- Communication – Language models can help students refine their writing and improve clarity in expressing ideas.
- Creativity – Generative AI tools can inspire students to compose music, design graphics, or brainstorm unique solutions.
- Critical Thinking – By prompting students to evaluate AI-generated content, we encourage scepticism and analysis.
- Citizenship – Teaching digital citizenship includes understanding the ethical implications of AI use.
- Character Education – Honesty, integrity, and empathy must guide how we and our students engage with AI.
Ideas for integrating AI in the school curriculum
MATHEMATICS: AI as a Problem-Solving Partner
- AI vs. Human: The Math Battle!
Goal: Teach students to analyze AI-generated solutions and develop their own problem-solving skills.
Activity Steps:
- Teachers give students a complex math problem.
- Students solve it on their own first.
- They then ask AI (ChatGPT, Wolfram Alpha, or Photomath) for a solution.
-
Compare answers:
- Did AI make mistakes?
- Did AI use a different method?
- Which solution is clearer?
- Final Task: Students write a reflection on when AI can help and when it might mislead.
Outcome: Students use AI as a learning tool rather than relying on it to do their work.

- AI-Generated Word Problems Challenge
Goal: Help students create and analyze real-world math problems using AI.
Activity Steps:
- Ask AI to generate a word problem based on a real-world scenario (e.g., sports statistics, shopping discounts).
- Students solve the problem and check if the AI’s numbers are reasonable.
-
Their challenge:
- Rewrite the problem more clearly if needed.
- Create their own, better real-life math problem for AI to solve.
- Final Task: Present both AI-generated and student-created problems to the class.
Outcome: Students practice problem formulation, reasoning, and real-world math applications.
- AI as a Math Tutor – But Is It Always Right?
Goal: Teach students to analyze AI explanations instead of blindly accepting them.
Activity Steps:
- Students ask AI to explain a math concept (e.g., fractions, algebra).
-
Their task:
- Rate the explanation (clear? correct? confusing?)
- Improve it using their own words.
- Pair Work: Compare AI explanations with textbook or teacher explanations.
Outcome: Students become active learners instead of passive AI users.
LANGUAGES: AI as a Writing Coach & Conversational Partner
- AI-Powered Storytelling Relay
Goal: Encourage creativity and critical editing skills.
Activity Steps:
- Students write the first paragraph of a story.
- AI writes the next paragraph.
- Students analyze and edit AI’s paragraph to match style, tone, and improve storytelling.
- The process repeats until the story is finished!
Outcome: Students practice writing, editing, and storytelling while keeping control over the content.

- AI as a Foreign Language Conversation Partner
Goal: Use AI chatbots for language practice and pronunciation improvement.
Activity Steps:
- Students chat with AI in a foreign language (e.g., Spanish, French, German).
- They correct AI’s mistakes or identify weird phrasing.
- Use AI-generated sentences for a role-playing scenario (e.g., ordering food in a restaurant).
- Bonus: AI-generated tongue twisters for pronunciation practice!
Outcome: Students practice speaking, listening, and correcting language errors in an engaging way.
- AI-Powered Poetry & Songwriting Challenge
Goal: Explore literary techniques using AI.
Activity Steps:
- Students ask AI to write a poem or song lyrics on a theme.
-
Their task:
- Identify rhyme schemes, metaphors, and literary devices.
- Rewrite the poem/song in their own unique style.
- Performance Time! – Students read or sing their revised versions.
Outcome: Students analyze AI-generated language while expressing their own creativity.
PHYSICAL EDUCATION (PE): AI for Sports Strategy & Fitness
- AI as a Virtual Sports Coach
Goal: Use AI to analyze game strategies and fitness training.
Activity Steps:
- Students ask AI for game strategies (e.g., best formations in soccer, basketball plays).
- They test AI’s strategies in practice.
-
Discussion:
- Did the AI strategy work in real life?
- What would they change?
- Can AI predict sports outcomes accurately?
Outcome: Students learn sports strategy and critical analysis using AI as a coach.
- AI-Personalized Fitness Plans
Goal: Teach students how AI can create but not replace personalized fitness training.
Activity Steps:
- Students input their fitness goals into AI (e.g., “I want to improve endurance” or “I need a 10-minute workout”).
- AI generates a custom workout plan.
-
Their task:
- Evaluate if the workout is realistic and safe.
- Modify it to make it better and more balanced.
Outcome: Students learn how to use AI for health and fitness safely and critically.
RELIGION & ETHICS: AI for Ethical Thinking & Moral Dilemmas
- AI & Ethical Dilemmas Debate
Goal: Explore ethical questions about AI and humanity.
Activity Steps:
- AI presents a moral dilemma (e.g., “Should robots have rights?”).
- Students debate AI’s response and compare it with ethical principles from their religion or philosophy.
- Bonus: Ask AI for religious perspectives on the issue and fact-check its accuracy.
Outcome: Students critically engage with AI-generated ethics and philosophy.
- AI vs. Sacred Texts – What’s Missing?
Goal: Help students compare AI-generated moral lessons with religious teachings.
Activity Steps:
- Ask AI to summarize a moral lesson (e.g., forgiveness, kindness).
- Compare AI’s version with religious texts (Bible, Quran, Torah, etc.).
-
Discussion:
- What’s missing?
- Can AI understand deeper spiritual meanings?
- How does AI’s version differ from human wisdom?
Outcome: Students reflect on the role of AI in understanding values and spirituality.

Day 6 – Discovering Trastevere
After five intensive days, the sixth day offered a different kind of learning: a guided outdoor cultural experience in Trastevere, one of Rome’s most authentic and vibrant neighborhoods. As we wandered through narrow cobbled streets, visited local artisan shops, and shared a traditional Roman lunch, we reflected on how education, like the city itself, is a blend of old and new.
Conversations flowed easily- about challenges at home, school reforms, and how to take this learning back to our students and colleagues. The informal setting reinforced the power of peer connection and cross-cultural exchange- hallmarks of the Erasmus+ spirit.
Taking it Home
Now back in our respective countries, we return not only with new digital tools and strategies but with a sharper understanding of the role of AI in education. We carry a renewed sense of responsibility to help our students navigate an AI-rich world with wisdom, integrity, and creativity.
We also bring back inspiration to support colleagues-especially those hesitant about AI-through dialogue, modelling, and shared resources. We will advocate for ethical, inclusive, and human-centred AI practices that reinforce-not replace-deep learning.
Final Thoughts
This Erasmus+ experience in Rome reminded us that while AI is transforming education, it is the human connections-between teacher and student, between colleagues, and across cultures-that truly prepare learners for the future. I must say that having more than 10 training courses over the past 4 years, this one was by far the best, due to our trainer being so diligently prepared and enthusiastic in his interactions, he was truly inspiring!
As Leonardo wisely said in our final session:“Let AI be the assistant, not the teacher. The heart of education is still-and always will be-the human mind and soul.”
This course was fully financed by Erasmus + funding and the statements in this article reflect the work and thoughts of the participant.
Written by: Steve Szabó
Avicenna International College, Budapest
03. June. 2025